Locking Kernel32.dll As Anti-Debugging Technique
[Edited: The technique discussed in this diary is not mine and has been used without proper citation of the original author]
For bad guys, the implementation of techniques to prevent Security Analysts to perform their job is key! The idea is to make our life more difficult (read: "frustrating"). There are plenty of techniques that can be implemented[1] but it's an ever-ongoing process. Note that this topic is covered in the SANS FOR610[2] training.
An anti-debugging technique is based on the following steps:
1. To try to perform a specific action
2. To test the result with a branching instruction
3. To execute some code to defeat the analyst (exit the process, return a false value, lock the GUI or generate an exception (crash)
The example that I'll cover in this diary was the subject of a thread on a security mailing list and I found it interesting enough to be reported here (I'm just wrapping up the information here, this is not a personal finding).
The sample has the following SHA256 hash: 68af250429833d0b15d44052637caec2afbe18169fee084ee0ef4330661cce9c[3].
If you run the sample into a debugger, you'll see that it exits with an exception error but, when executed in a sandbox, it works like a charm. Let's see what's the magic behind this.
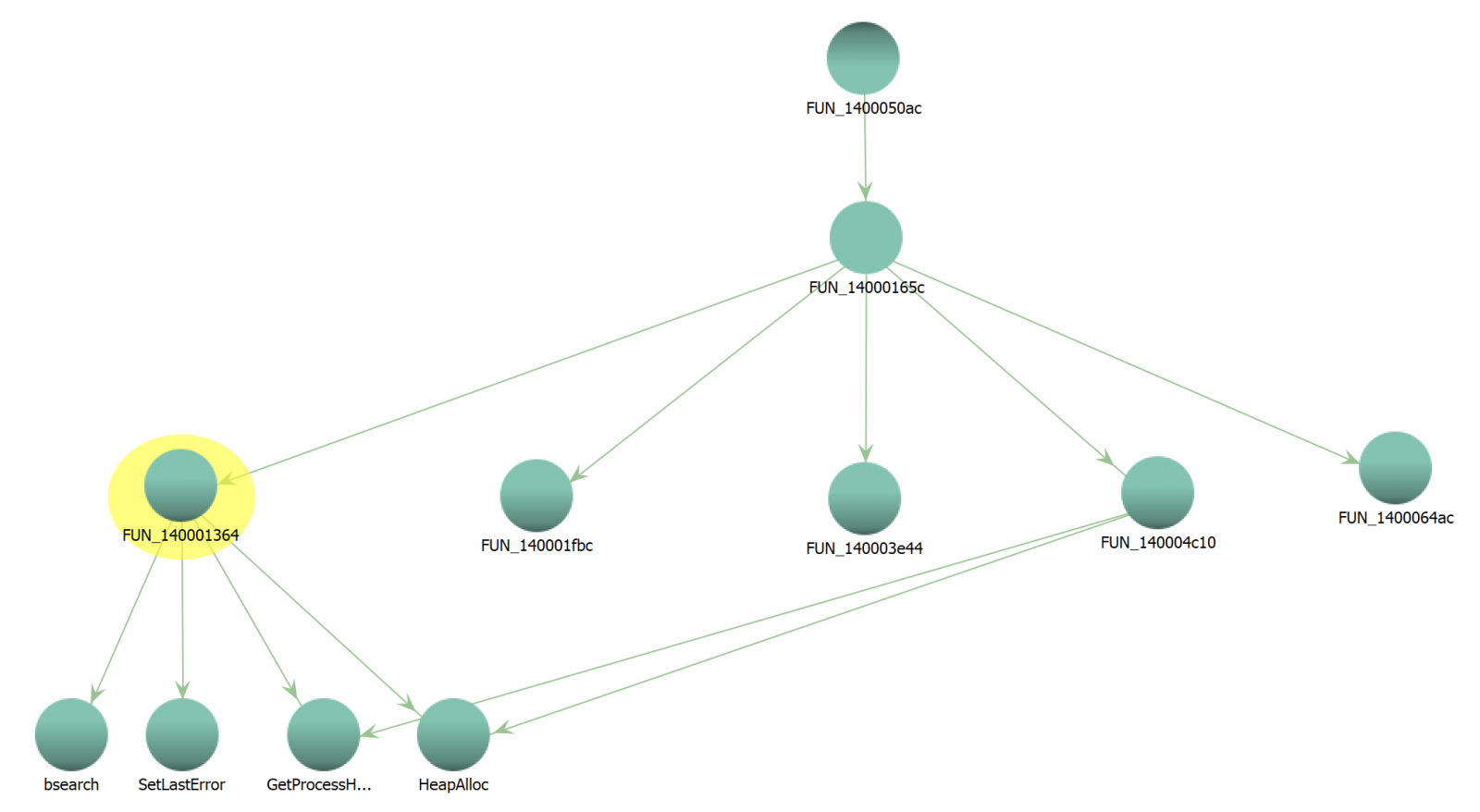
The exception occurs in a function FUN_140001364(). This function is called multiple times from FUN_14000165C() as seen on the graph below:
First, we have an obfuscation technique based on stack strings but with a shift of characters:
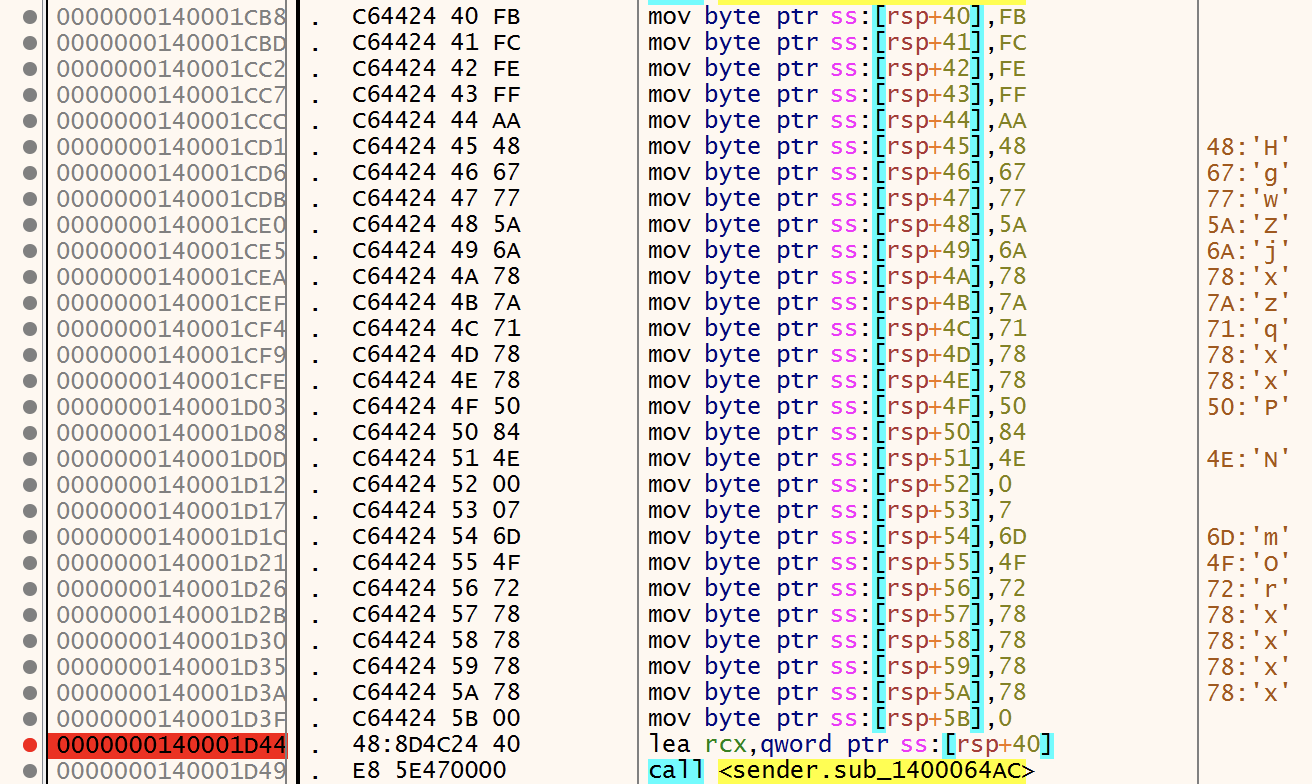
The string 'HgwZjxzqxxP...' can be decoded with this Python code block:
>>> s='HgwZjxzqxxP' >>> d='' >>> i=1 >>> for c in s: ... d = d + chr(ord(c)-i) ... i=i+1 ... >>> d 'GetVersionE'
The function FUN_140001364() expects two arguments:
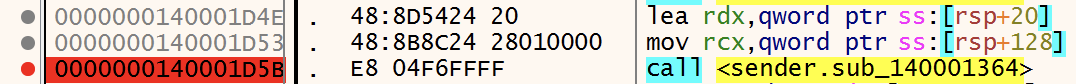
Basically, it's a kind of GetProcAddress() replacement. The first argument is a pointer to the DLL to search and the second argument is the function to search in this DLL. But, when executed in a debugger, the first argument is NULL and it causes the exception.
The question is now: why is this pointer set to NULL? We know how the anti-debugging works but how is it triggered?
In the function FUN_140001FBC(), we see a call to CreateFileW(). According to the Microsoft documentation, it expects 7 parameters[4]:
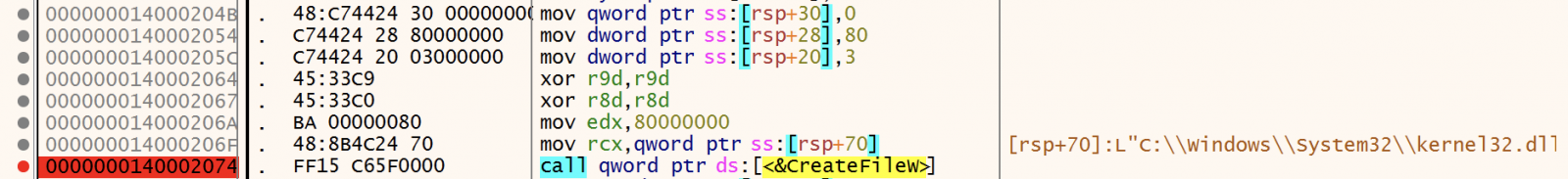
The first argument is the filename to work with. Very interesting, despite the function name, CreateFileW() can be used to create or OPEN files. In this case, the malware tries to open the Kernel32 DLL and read the content in memory. The file is opened in exclusive mode (dwShareMode is zeroed). From the documentation:
"If this parameter is zero and CreateFileW succeeds, the file or device cannot be shared and cannot be opened again until the handle to the file or device is closed".
This causes a problem with the debugger and CreateFileW() fails (RAX - the return value - contains 0xFFFFFFFF). The file won't be read and the execution continues until FUN_140001364() is called with a bad pointer and crashes.
To bypass this problem, an interesting technique was proposed in the discussion: Let's duplicate kernel32.dll on the filesystem and rename it kernel33.dll. Then, just before the call to CreateFileW(), patch the memory and replace the filename:
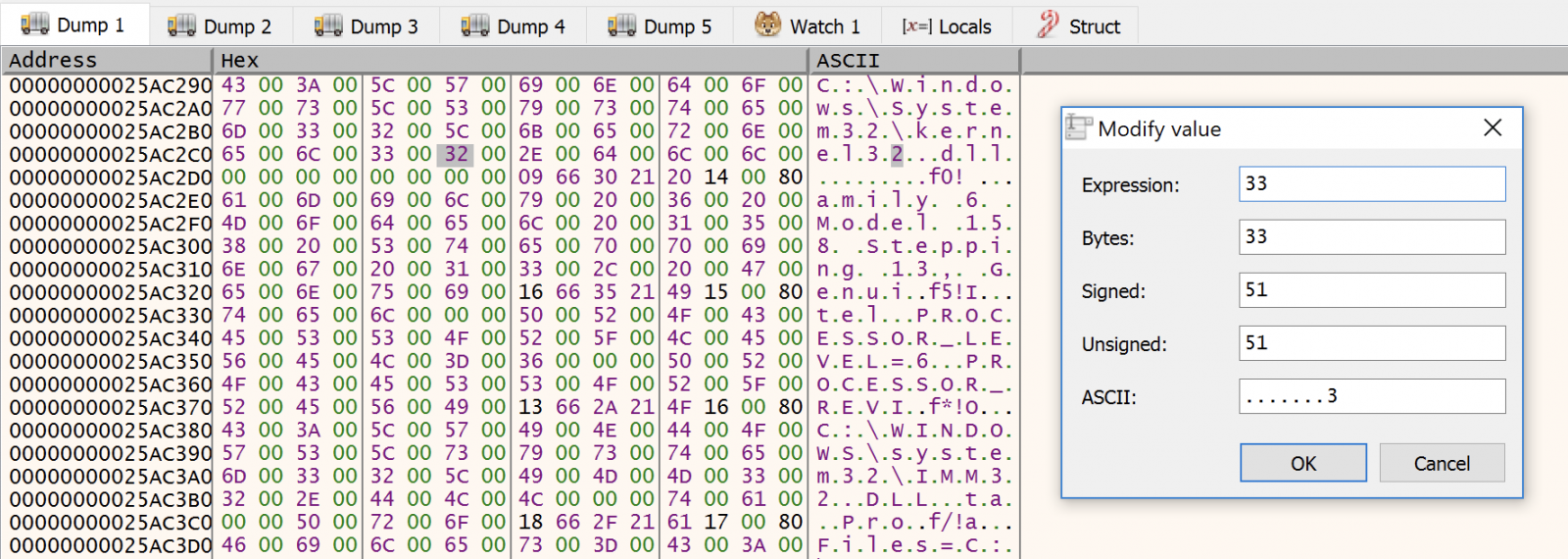
Now you can do your job and continue to debug the sample. To conclude, here is another interesting technique used by the malware to cover its track. It overwrites the file that launched the sample with 0's and deletes it by calling a Powershell command:
$ppid = (gwmi win32_process | ? processid -eq $PID).parentprocessid; $proc = Get-Process -FileVersionInfo -Id $ppid; Stop-Process -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue -Id $ppid; $buff = [byte[]]@(, 0 * 1mb); Set-Content -Path $proc.FileName -Force -Confirm:0 -Value $buff; Remove-Item -Path $proc.FileName -Force -Confirm:0
[1] https://search.unprotect.it/map/
[2] http://for610.com
[3] https://bazaar.abuse.ch/sample/68af250429833d0b15d44052637caec2afbe18169fee084ee0ef4330661cce9c/
[4] https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/fileapi/nf-fileapi-createfilew
Xavier Mertens (@xme)
Senior ISC Handler - Freelance Cyber Security Consultant
PGP Key
| Reverse-Engineering Malware: Advanced Code Analysis | Online | British Summer Time | Jul 28th - Aug 1st 2025 |



Comments